Early Civilizations 101: The Inca

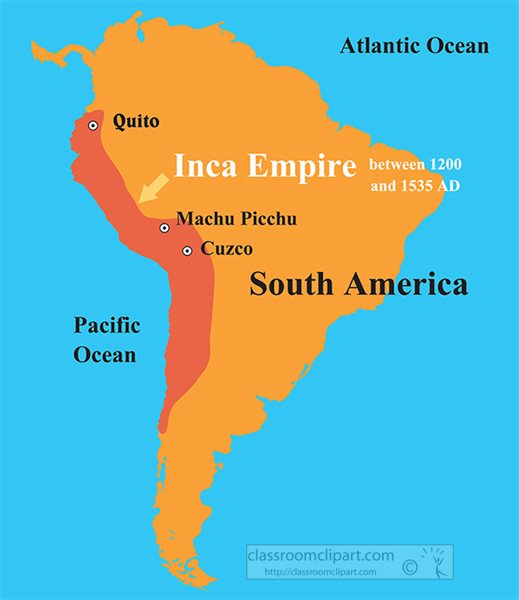
The Inca civilization existed between the 12th and 16th centuries in the Amazon region, now bordering Ecuador, Peru and Chile. The Incas, a tribal community, lived in the Andes Mountains in South America and established a great empire. Since the hot, humid and rainy parts of the equatorial climate are not suitable for living, they have chosen high places as their habitat.
It has known that the Incas have similarities with the Egyptian Civilization in many areas. Their divine beliefs and posthumous life issues can be given as examples. Mummified human remains have been found in many archaeological excavations belonging to the Incas, who believed in life after death. Just like in the Egyptian Civilization, these mummies are buried with valuable items and dedications are made to them. This is a testament to their divine belief and to the belief in the afterlife. At the same time, it is noteworthy that the settlements are close to the sky.
 (Credit: Inca Gold Sun Mask. (Andrew Howe) Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. )
(Credit: Inca Gold Sun Mask. (Andrew Howe) Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike. )
As an example of their godly beliefs, according to legend, the ancestors of the Inca rulers were created by the God of Sun, Inti and appeared in a cave called Tambo Toco. Leading his four brothers and four sisters, Ayar Manco carried the golden staff with instructions. And his goal was to find the place where the wand could sink to the ground and show the fertile land. After many adventures and searches, Ayar Manco and his brothers reached to the Cuzco Valley, the land pierced by the wand. They founded their capital after a fierce war with the local population, and the Setting Manco; Manco Cabac became the first Sapa Inca, the King of the Incas. Being the founder of civilization, this emperor made the Incas an advanced civilization in many areas in a short time.

(Credit: A portrait of Manco Capac, first Inca ruler. Lilly Library: Latin American mss. Peru.)
The Inca people built gigantic administrative units, temples, wide roads, and canal systems over a large area of kilometers. They did all of them in an inhospitable landscape without wheels, horse, iron or even a written language. This society, which was also in an advanced position in the architectural field, turned the stones into a work of art and established cities on the slopes. These incredible cities that were founded still attract the attention of archaeologists and researchers today. Especially, it is a matter of curiosity how the huge stone blocks were transported and placed with the technology of that time.
 (Credit: Machu Picchu Aerial View. Mark Cartwright. Creative Commons Attribution )
(Credit: Machu Picchu Aerial View. Mark Cartwright. Creative Commons Attribution )
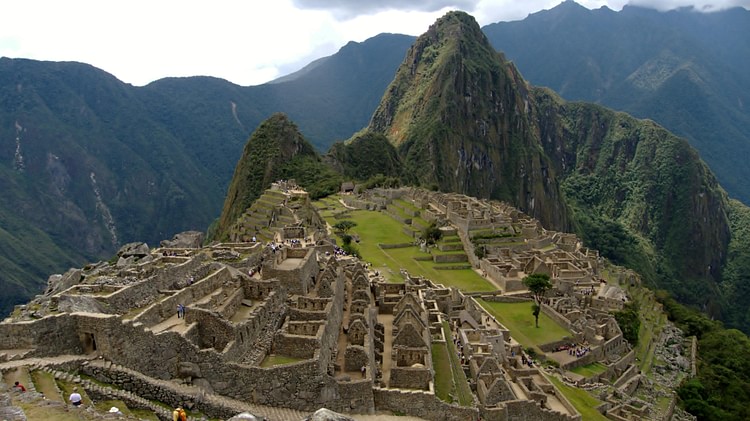
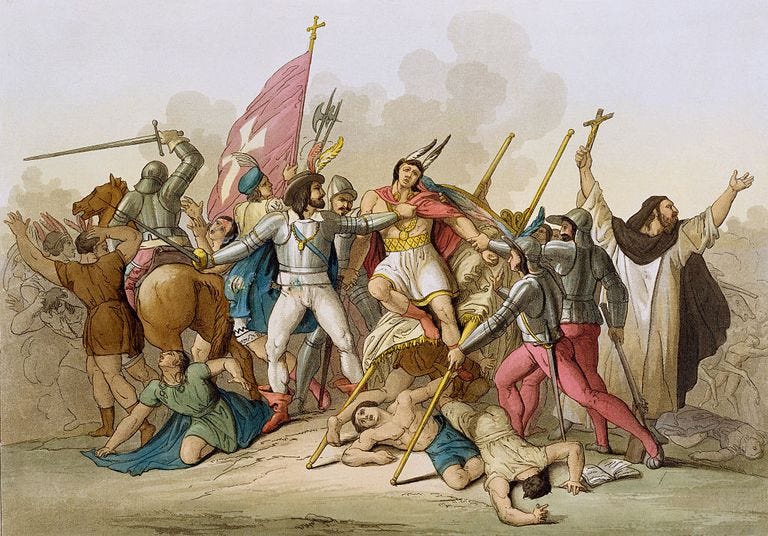
The following question is usually asked about one of the cities built by the Inca civilization full of mysteries; “How and why was the Inca civilization unable to find the wheel and writing, but able to built an engineering wonder city like Machu Picchu around 1450?” This city, one of the 7 wonders of the world, was built around 1450 by Pachacutec Yupanqui, the ruler of the Incas, one of the indigenous peoples of South America, at the summit of the Andes in Peru, at an altitude of 2360 meters. Nearly 100 years after the establishment of civilization, geographical discoveries and invasions made by European states in America tried to destroy civilization and indigenous people. The Incas tragically disappeared in a short time.

(Credit: Spanish conquest of Peru. https://www.thoughtco.com/thmb/2bUTuML6uBeZ_5Wtd_CYgtpwZHk=/768×0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/19th-century-print-a-soldier-grasps-atahalpa-king-of-the-incas-534290974-58e094af5f9b58ef7ea1733b.jpg )
During the Spanish invasion, which took place in 1532 and caused the collapse of the Inca Civilization, the city of Machu Picchu was not noticed thanks to its geographical location and has been carried to the present day. It still has ruins. Thousands of tourists annually visit this place to breathe the mystical atmosphere of the Inca Empire and to carry a piece of it.
Sources:
Britannica, T. Editors of Encyclopaedia (2020, May 5). Inca. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Inca
Cartwright, M. (2014, September 15). Inca Civilization. World History Encyclopedia. Retrieved from https://www.worldhistory.org/Inca_Civilization/
Ekoyapı. (2019, May 21). Antik ve Yeşil Rota: Machu Picchu. https://www.ekoyapidergisi.org/6112-antik-ve-yesil-rota-machu-picchu.html
Coğrafyacı. İnka Uygarlığı. https://www.cografyaci.gen.tr/inka-uygarligi/
Adım Adım Tarih. (2021, February 5). İnka Uygarlığı. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=as4XLHNiNDk
tarihiolay.com. (2020, April 30). İnka Medeniyeti: İnkalar Kimdir?. https://tarihiolay.com/medeniyetler-tarihi/amerika-medeniyetleri/inka-medeniyeti/







